Stay ahead of the curve with the latest news, ideas and resources on all things Identity Assurance and Passwordless.
What is Passwordless Authentication?



Passwords remain the most vulnerable and most attacked part of any authentication system. They pose a risk not just to authentication security but to an organization’s security posture as a whole. For example, Verizon's DBIR report found that over 60% of the actions leading to successful attacks were connected to credentials (e.g., phishing, use of stolen credentials, brute-force attacks).
The considerable problem with passwords and all shared secrets comes down to the fact that if they can be shared between two parties, they can ultimately be shared with the world. According to Darkreading.com there are now more than 24 billion stolen credentials circulating on dark web marketplaces. As Microsoft's CISO, Bret Arsenault, puts it, "Hackers don't break in, they log in." The only way to shift that paradigm is to completely eliminate passwords from authentication. This is where passwordless authentication approaches, particularly phishing-resistant MFA solutions, come in. But what is passwordless authentication and what does a world without passwords look like?
Passwordless Authentication Overview
Legacy single-factor authentication is based on proving identity with a username and password pair. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) requires one or more independent verification factors. These can be something you know (such as a password or secret question), something you have (such as a security key or an OTP sent to a device), something you are (a biometric feature such as face recognition or fingerprint). In traditional MFA, this is generally a password plus another factor.
Passwordless authentication, on the other hand, removes the password (and any knowledge factor) as an acceptable proof of identity, using only "possession" or "inherence" factors. You can have single-factor (e.g., an OTP or YubiKey) or multi-factor passwordless authentication (e.g., a solution like HYPR).
While traditional MFA is more secure than just a password, many systems, such as those relying on push notifications or SMS OTP, are easily circumvented by attackers. So, what is passwordless authentication doing differently than other MFA to prevent these types of authentication attacks? Depending on the passwordless approach, it may not be. Some ostensibly passwordless solutions use shared secrets such as OTPs for login. Others store and use centralized credentials on the back end. Fully passwordless authentication, however, completely eliminates shared secrets from every aspect of the authentication process and is much more secure than legacy MFA. Passwordless MFA based on FIDO specifications is considered the gold-standard for phishing-resistant MFA.
Here's an example of how it works, based on a passwordless authentication system using public key cryptography and a mobile authenticator client app:
- User begins login process
- Passwordless authentication system requests identification factors
- User unlocks the private key with their passwordless authenticator
- At the server end, the public key of the public-private key pair is used to certify the secure identity
- User is granted entry
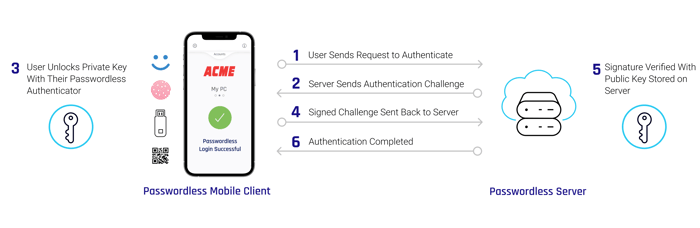
As can be seen from this process, the user is not required to provide anything but the device they have (possession) and their thumb print (inherence). They meet the MFA threshold without ever having to remember or share a password.
Due to the cryptographic complexity and the processes used in public key encryption, there are no secrets or credentials that can be intercepted by eavesdropping or leveraged in man-in-the-middle attacks. And of course, a hacker can't access an account by guessing or phishing a password.
How Does Passwordless Authentication Work?
Technological advances and the ubiquity of biometric identifiers on smart devices mean that passwordless technology can be deployed for virtually any authentication point. This is especially relevant as remote desktop protocol (RDP) and virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI) have become a much larger factor in many organizations' security posture since the COVID-19 pandemic and the resultant shift to remote work.
Organizations typically work with many applications, some SSO-connected, some not. Passwordless authentication can be used to log into your SSO to gain secure access to connected applications, as well as be integrated with many non-SSO applications and tools.
Passwordless authentication can also solve the desktop MFA security gap. Laptops, workstations and server logins are often protected by just a username and password, leaving them vulnerable to data theft and being used as a gateway for system attacks. Implementing traditional MFA at the desktop often causes usability and security issues — employees may not lock unattended devices in order to avoid clunky, time-consuming logins when they return. Some passwordless authentication systems offer the ability to protect desktop as well as application logins.
In addition, passwordless technology can be integrated into customer-facing web and mobile applications, making them harder for attackers to access.
Changing the Security Paradigm: Is Passwordless Authentication Safe?
Despite guidance from the federal government and major tech providers, phishing-resistant MFA still remains to receive major uptake. Often organizations ask, "what is passwordless authentication capable of providing that other MFA doesn't?" The answer isn't necessarily in what it does, though that can be highly innovative; it's also about what it doesn't do.
Since going "passwordless" removes the key pain point in authentication systems, it brings an immediate and measurable positive impact to an organization's security, IT and business operations. First and foremost, it automatically improves organizational security by eliminating the single biggest vector of attack. Microsoft, which reports over 300 million fraudulent login attempts a day to its various products, states that combining biometrics and possession authentication blocks 99.9% of attacks aiming to compromise accounts. With increasing regulation regarding data safety, deploying passwordless MFA also helps organizations achieve compliance and reduce overall risk.
Other benefits include cutting password reset costs, which, according to Forrester, cost an organization $40 – $50 per password reset. Passwordless authentication can also simplify the user experience and increase productivity. Finally, passwordless authentication assures compliance with MFA insurance standards many cyber liability insurance carriers set forth.
To learn more about passwordless security and its benefits, download the Passwordless 101 guide.
The Next Step Towards Passwordless with HYPR
Passwordless authentication improves security for your users, systems and organizations by removing the weakest link in the authentication process. Anyone wondering, “What is passwordless authentication able to deliver?” should look to the industry's leading passwordless MFA.
HYPR's True Passwordless™ MFA significantly hardens your authentication security while improving productivity and user buy-in. Based on public key cryptography and adhering to FIDO standards across all components, it ensures there are no shared secrets at any point in the authentication process. HYPR delivers a single seamless desktop-to-cloud authentication flow that alleviates user-experience frustrations around authentication. To see how HYPR’s passwordless solution can help your organization secure authentication and access, talk to our team.
Joshua Gonzales
Senior Product Marketing Manager
Joshua Gonzales is a Senior Product Marketing Manager at HYPR, where he helps position the company’s authentication solutions in the identity security space. He previously led go-to-market strategies at cybersecurity companies such as Beyond Identity, and also worked as a social media consultant for major brands including HarperCollins and Express. Joshua’s background in cybersecurity and digital storytelling helps convey the importance of eliminating passwords and building trust in the identity lifecycle.
Related Content
