Stay ahead of the curve with the latest news, ideas and resources on all things Identity Assurance and Passwordless.
Using Deterministic Security Controls To Stop Generative AI Attacks



Deepfake cyberattacks, phishing, and social engineering have all received a turbo boost in recent months due to the proliferation of easily accessed AI tools. Cybercriminals are some of the most creative individuals in the world. They spend their days conjuring up different ways to bypass security systems, not filling out spreadsheets and reports.
In this article, we discuss how hackers are leveraging AI tools to bypass traditional identity security controls at an unprecedented pace, and just why generative AI attacks are so successful. We also look at how these attacks can be defeated using identity assurance controls that take a deterministic approach to securing identities, rather than relying on probabilistic methods that contain inherent levels of uncertainty. By implementing these modern controls, organizations can significantly reduce their risk of identity fraud for both their workforce as well as customers.
Common Generative AI Attacks
Hackers use out of the box as well as specifically trained large language models (LLMs), often created by nation state hackers (China, Russia, North Korea), to execute cyberattacks with frightening accuracy. Here are some of the attacks that get a significant boost from AI.
Phishing
Prior to AI, we used to frequently delineate between “phishing” and “spear phishing,” where attacks were tailored to a specific individual. By using LLMs, hackers are now able to tailor just about every single phishing message to a specific target to get a much higher success rate. For decades now the industry has trained employees to spot telltale signs of phishing by looking for grammatical and spelling errors. Today, phishing messages created by LLMs are in the local language, contain local context, and are largely indistinguishable from the legitimate messages users get every single day. A recent study found a 1,265% rise in phishing, largely due to the usage of AI tools.
Impersonation (Deepfake Cyberattacks)
Identity theft is at an all time high due to the ability of AI to impersonate an individual across all communication channels including voice, text and video. In recent weeks, a scammer used a series of video deepfakes to extract more than $25M from an organization. Hackers can create personas based on individuals in minutes, merely by looking at samples of their writing, publicly available videos, and social media posts. Just a few years ago, creating a deepfake video required significant resources. Today, freely available apps can do the job fairly well, with accuracy improving by leaps and bounds daily.
Social Engineering
Before AI, social engineering attacks were highly manual in nature and oftentimes had low success rates. We’ve all received scam calls and many of us can easily spot them when the caller has no knowledge of our details and speaks with an unfamiliar accent. By using AI, hackers are able to create chatbots and voice conversation systems that mimic the tone, cadence, and contextual nuances of a specific target audience. LLMs also are able to use reinforcement learning so that they get better with every single conversation that occurs. These improved algorithms can then be used to target large numbers of users simultaneously, rather than being bottlenecked by human interactions.
Why Generative AI Attacks Are Successful
Hackers love AI tools because they make them more efficient than ever. There are a few key reasons why AI-assisted attacks are seeing so much success today:
Speed and Scalability
AI can process and analyze data and conversations at speeds that outpace any human by orders of magnitude. This ability enables these tools to launch widespread attacks in a very short amount of time.
Adaptability
AI systems can adapt their strategies based on the responses from the target’s defenses. If users have been trained to look for specific red flags, these tools can adapt and respond accordingly within seconds. As a result, defense systems that rely on blocking known attack patterns are trivial for an AI attack to bypass quickly.
Efficiency in Targeting
AI can analyze data from various sources to identify the most valuable targets to maximize its success. When AI identifies a series of patterns or signals, it can quickly train itself to focus on targets with the most likelihood for success. Most importantly, it can correlate with other AI systems who “soften the target,” to then outflank victim organizations' security controls. For example, one AI tool can target an organization with a DDOS attack and, when the victim is busy responding, another AI tool can execute a highly contextualized phishing campaign that references the DDOS attack to maximize its success rate.
Leveraging Big Data
AI systems are able to integrate with countless data sources both public and private in order to maximize their impact. Attackers leveraging AI can refine strategies within seconds based on real-time events in ways never possible before. Social media, previous breach data available on the dark web, and leaked credentials can all be processed instantaneously to create new and more sophisticated attacks with a high likelihood of success.
Why Probabilistic Identity Security Controls Fail Against an AI Attack
The vast majority of identity security controls are failing today. To understand why this is the case, we have to understand the probabilistic nature of their implementations.
Probabilistic security controls operate on the basis of likelihood. They use various criteria to determine the probability that something is safe or a potential security threat. By contrast, deterministic security controls identify an outcome with a binary level of precision. They can determine with a high degree of certainty if something is true or false, safe or a threat.
With this in mind, let’s look at some of the primary methods the industry uses today to prove that someone is who they say they are.
Phishable Authentication Factors
Passwords, one time passwords (OTP) delivered via SMS or app, and push notifications are the primary methods organizations use to verify users today into their systems. AI creates significant accuracy in brute force password spraying attacks by being able to predict passwords. It also strengthens phishing and social engineering to trick users into providing OTP codes or accepting push notifications at a high rate. These controls are probabilistic as they cannot determine with certainty that the entity seeking access is the legitimate credential holder, and can be intercepted, replayed and phished.
KBA-Based Identity Verification
AI systems’ ability to ingest massive amounts of data extremely quickly and in real time enables them to learn about their targets and easily answer questions such as their mother's maiden name and the street they grew up on. By combining this with phishing and social engineering capabilities, these AI-assisted hackers can quickly execute identity theft and gain access to employee and customer accounts. Knowledge-based security methods are also probabilistic by nature and can be easily intercepted, replayed, and phished from users.
Human-Verified Documents
Many businesses have moved from KBA to online or in-person document verification in order to reduce identity fraud. However, attackers can use widely available AI tools to create fake documents such as passports and driver licenses that are able to trick most systems. The image below is a fake passport generated by AI that was able to bypass the identity verification system of a cryptocurrency exchange.

Image Source: 404 Media
Both human and machine-based verification controls of documents are probabilistic in nature because they have to account for differences in documents with regard to image quality and the sheer number of variations of the documents themselves. They can only determine the likelihood that a document is legitimate.
Five Identity Controls to Defend Against AI Attacks
1. Focus on Deterministic Controls
In recent years, deterministic controls to secure identities have started to enter the market by way of open standards and innovative technology companies. Unlike most probabilistic controls, deterministic identity technology plays a crucial role in countering AI-assisted cyber attacks because they can provide a binary certainty; a definitive yes or no that eliminates the gaps exploited by AI-assisted attacks.
2. Strong Authentication Protocols
Cryptographic Techniques: FIDO and similar protocols, such as the traditional smartcard, use public-key cryptography for authentication. During the registration process, the user’s device creates a new public-private key pair. The private key is kept secret on the device, while the public key is registered with the online service. Authentication involves proving possession of the private key without it ever leaving the user's device, making it extremely difficult for attackers (AI-assisted or not) to steal or replicate.
Biometric Verification: FIDO, for example, supports local biometric verification (like fingerprint sensors, facial recognition, etc.), which are difficult for AI to fake because the biometric data is not transmitted over the network. Instead, the device confirms the match and then uses cryptographic keys to authenticate the user to the service.
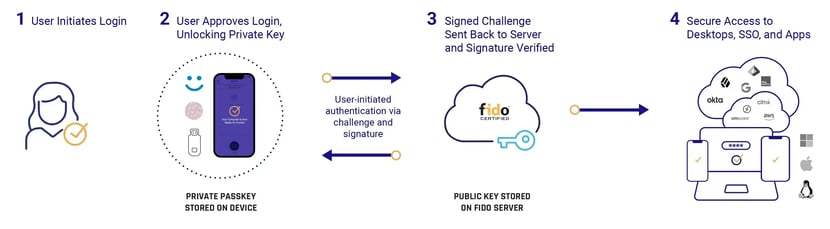
Phishing Resistance: FIDO authentication is bound to the original website's URL, making it resistant to phishing attacks. Even if AI is used to create highly convincing phishing sites, the authentication process checks the URL to ensure it matches the registered service’s URL, preventing the credentials from being used to authenticate a fraudulent site.
Local Storage of Credentials: Since the cryptographic credentials in FIDO are stored locally on the user's device and never shared with the server or across the network, AI-assisted attacks that rely on intercepting or deducing credentials remotely are rendered ineffective.
3. Layered IDV to Prevent Deepfake Cyber Attacks
Deepfakes are getting more sophisticated on a daily basis. While liveness detection is a positive step forward, it’s only a matter of time before it’s defeated by the rapid pace of innovation in AI. Multi-layered identity verification offers a deterministic way to prove people’s identities to defend against deepfake cyber attacks. Instead of relying purely on voice or video feeds, you combine a series of factors such as location, behavior, document verification and face recognition so that you can be certain that an identity is genuine.
4. AI-Assisted Identity Risk Mitigation
While deterministic security controls are essential, they cannot fully protect against unknown and emerging threats. Modern probabilistic identity security controls take advantage of the same AI assistance as attackers. Real-time risk assessment and adaptive security controls are a critical tool for organizations to manage evolving identity risks. By ingesting risk signals from a wide variety of sources, you can bring high fidelity to probabilistic controls.
5. A Collaborative Identity Security Stack
It’s no secret that many identity security solutions tackle very specific challenges, operating in isolated spheres. Generative AI attacks find and exploit the gaps between these fragmented identity security processes. Open standards like FIDO and Open Policy Agent (OPA), were developed, in part, to ensure compatibility between security tools and processes. A more unified identity security approach, with solutions that communicate and collaborate across the identity lifecycle, greatly decreases the success rates of generative AI attacks.
HYPR’s Anti-AI Strategy
HYPR was founded to put in place a deterministic way of proving that people are who they say they are. As a result, we were one of the first commercially successful implementations of the FIDO standards. Since then, our platform has expanded to prevent automation and scaling of identity-related attacks. Learn more about AI attack prevention from HYPR.
The HYPR Identity Assurance platform combines strong passwordless authentication, continuous risk mitigation and comprehensive identity verification so that you can be certain that a person is who they claim to be throughout the identity lifecycle.
HYPR Authenticate is our category-leading passwordless MFA solution, which is built on top of the FIDO standards and fully eliminates breachable credentials from your authentication and verification processes.
HYPR Adapt is an identity fabric, which integrates real-time risk assessment and mitigation, leveraging high-fidelity risk signals from numerous sources, including external environments, endpoints and other cybersecurity products.
HYPR Affirm, our comprehensive product for identity verification, provides a deterministic way to prove that an identity is legitimate and belongs to the person asserting it. HYPR Affirm combines a series of factors such as location, behavior, document verification, AI-powered chat, video, facial recognition and other cutting-edge technologies.
HYPR Affirm User Flow

To see how HYPR can protect your organization from deepfake cyberattacks and generative AI, arrange a personalized demo.
Bojan Simic
CEO, HYPR
Bojan Simic is the Chief Executive Officer & Co-Founder of HYPR. Bojan's vision for the elimination of shared secrets and his experience in authentication & cryptography serves as the underlying foundation for HYPR technology and company strategy. Previously, he served as an information security consultant for Fortune 500 enterprises in the financial and insurance verticals conducting security architecture reviews, threat modeling, and penetration testing. Bojan has a passion for deploying applied cryptography implementations across security-critical software in both the public and private sectors. Bojan also serves as HYPR’s delegate to the FIDO Alliance board of directors, empowering the alliance’s mission to rid the world of passwords.
Related Content